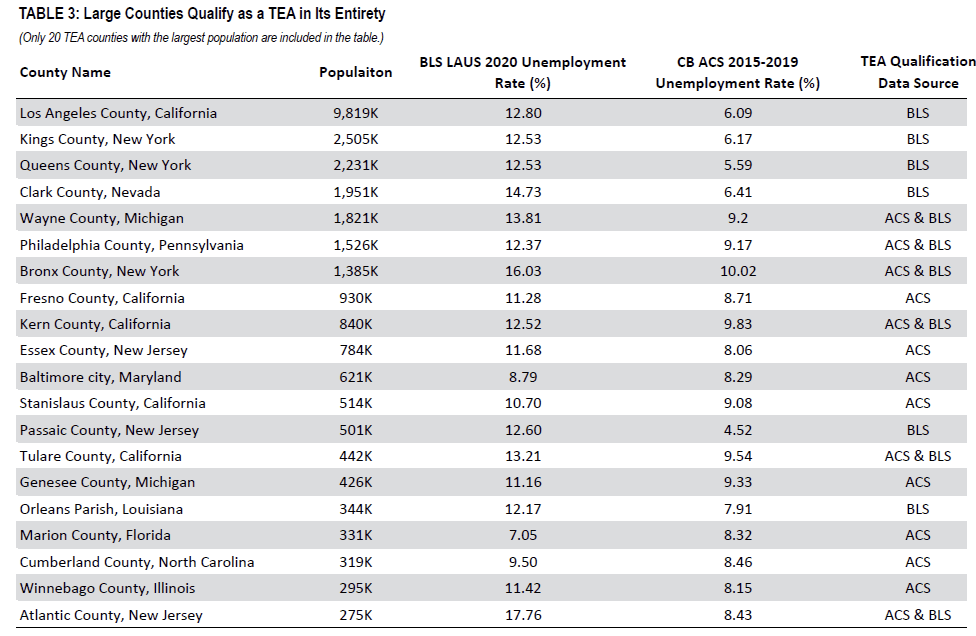by Lee Li, Director of Policy Research and Data Analytics, IIUSA
Article originally published in the May 2021 IIUSA Regional Center Business Journal

Lee Li is the Director of Policy Research and Data Analytics of Invest In the USA (IIUSA)
In April 2021, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) published the latest annual Local Area Unemployment Statistics (LAUS) for 2020. This data release is significant because it reflects the impact of COVID-19 on unemployment rates across the country. Additionally, the new set of employment data from BLS is even more consequential in the context of EB-5 given the fact that it changes the landscape of targeted employment areas (TEA) in urban America, affecting the geographic areas that are eligible for the lower minimum EB-5 investment amount. Based on the annual LAUS data for 2020, the national average unemployment rate is 8.05%, establishing the threshold of qualifying as a high unemployment area as 12.08% (150% of the national unemployment rate).
In addition to the LAUS data from BLS, the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) confirms that unemployment data published by the U.S. Census Bureau’s (CB) through the American Community Survey (ACS) also qualifies as “reliable and verifiable” to demonstrate TEA qualification for an area when an EB-5 investor files his/her form I-526 petition. However, the most current ACS data measures economic statistics in the U.S. between 2015 and 2019, which does not reflect how COVID-19 impacted the unemployment rate for American workers in 2020 and beyond. Based on the ACS 5-year estimates for 2015-2019, the national average unemployment rate is 5.33%, meaning that any area with an unemployment rate of 8.00% or higher will qualify as a high unemployment area, hence a TEA.
TEA Trends on National Level
Under the new EB-5 regulations that went into effect in November 2019, a TEA can be either a rural area or a high unemployment area. According to USCIS, a rural area is an area that is located outside 1) a metropolitan statistical area (MSA); or 2) any city or town with a population of 20,000 or more; while a high unemployment area could be any of the following areas if the area “has experienced an average unemployment rate of at least 150% of the national average unemployment rate:
- An MSA;
- A specific county in an MSA;
- A county in which a city or town with a population of 20,000 or more is located; or
- A city or town with a population of 20,000 or more outside of an MSA.
Additionally, the new regulations also introduced a new TEA method that allows a TEA to consist of a census tract or multiple contiguous census tracts as long as each one of the included tracts is directly adjacent to the project tract when calculating the weighted average unemployment rate for the entire area…Continue Reading